Foam Reorganization Mirrors AI Learning Mathematics, Study Finds
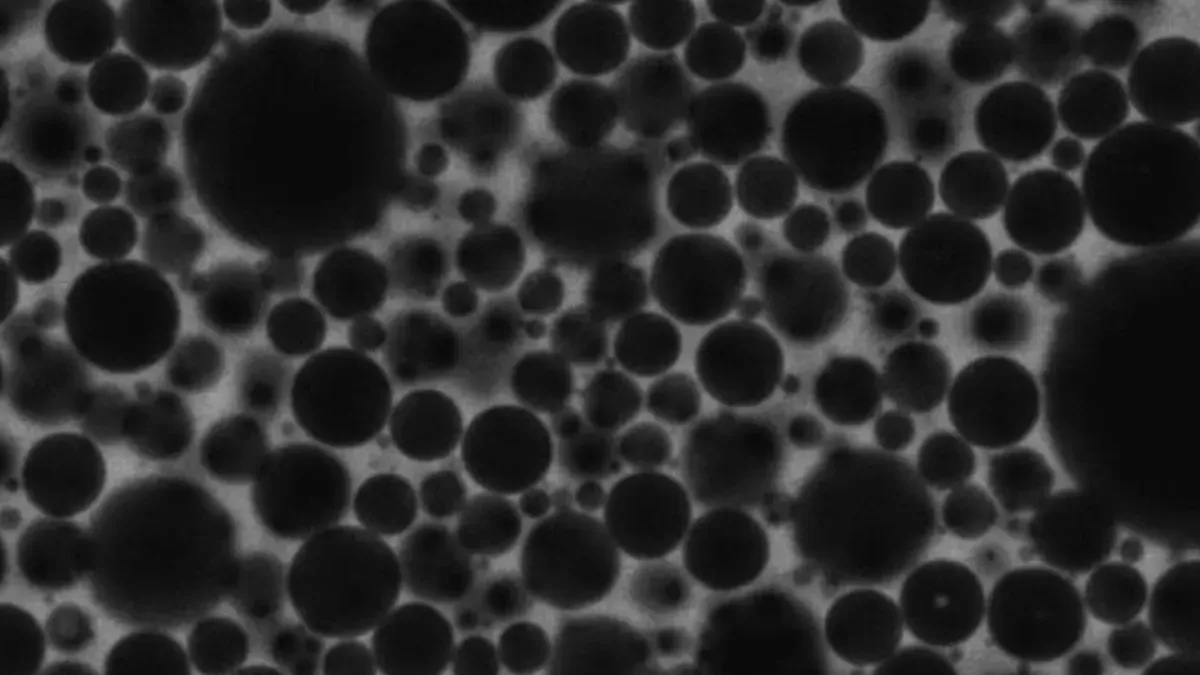
Foams may hold the key to understanding artificial intelligence’s secret logic. A new study reveals that foam dynamics at microscopic scales exhibit mathematical parallels with deep learning algorithms in AI, challenging traditional views of foams as static materials.
The research demonstrates that bubble movement in foams mirrors gradient descent methods used in AI training. This dynamic reorganization suggests a shared mathematical framework between physical systems and machine learning models.
John C. Crocker said:
"Foams constantly reorganize themselves. It's striking that foams and modern AI systems appear to follow the same mathematical principles."
Robert Riggleman added:
"Keeping it in flatter parts of the landscape, where lots of solutions perform similarly well, turns out to be what allows these models to generalize."
This computational model could inform understanding of adaptive biological systems like cell cytoskeletons. However, the study lacks experimental validation in biological contexts and provides theoretical insights rather than actionable health interventions.
⚠️ LEGAL DISCLAIMER: It is for informational purposes only. It never substitutes for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always consult your doctor regarding any questions about your health.




